Saturday, November 22, 2014
Saturday, November 8, 2014
Tuesday, September 23, 2014
Testing Framework - Predictive/Statistical
Independent testing includes majorly 5 components as depicted above. Each of the 5 components are further explained below taking the industry frameworks like PMBOK, ITIL, Six Sigma, Lean, Agile, CMMI Services etc.,
Similarly Usage or application of statistics can be grouped into 4 major categories as below.
Below diagram depicts few of the tools/techniques used in each of the above 4 categories.
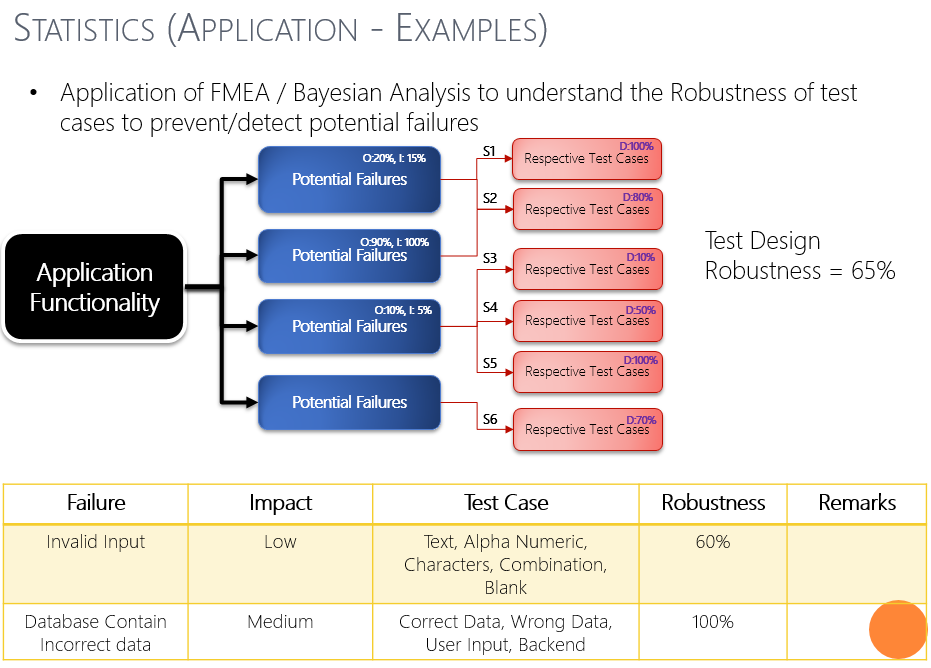
Below slides shows few of the examples in each of the above categories with the alignment to the testing scenarios/processes/metrics.
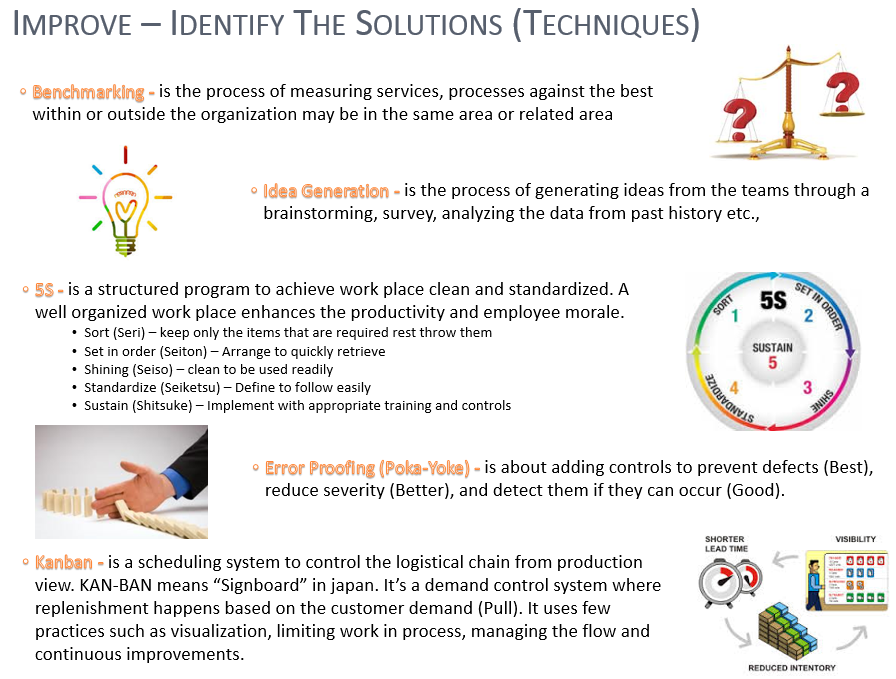
Below slides provides few more examples/models that can be applied in actual testing i.e., test case generation, test execution, test planning etc.,
Wednesday, August 6, 2014
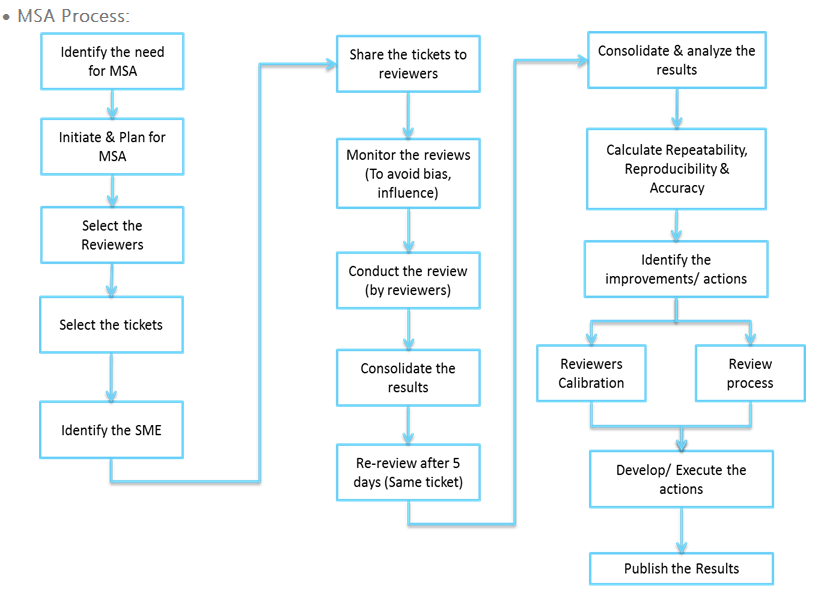
Six Sigma – Measurement System Analysis
Context: In this scenario the incident tickets were reviewed by
the selected and trained reviewers with respect to a predefined
parameters. The main objective is to
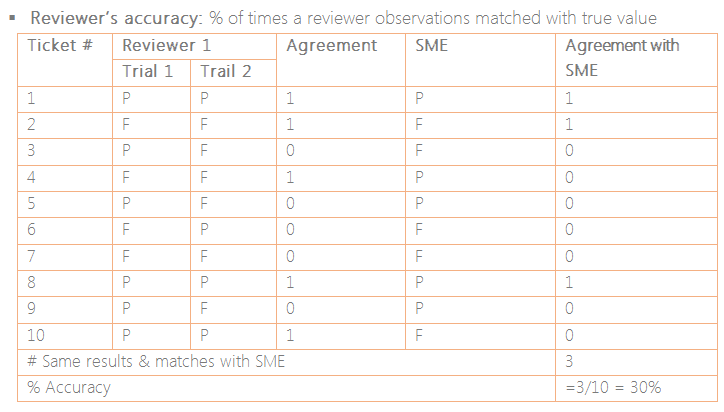
understand the accuracy as well as the consistency among the reviewers before
confirming the review results followed by appropriate actions.
v
Reviewers, Checklist, Environment, Review method, Data
collection/capturing
Components
of MSA Process:
·
Key Considerations:
§
The study should be performed over the range (Severities,
Shifts, Reviewers, Towers etc.,)
§
Actual Checklist should be used, already written review
procedures should be followed
§
It should be business as usual
§
Measurement variability should be presented “as-is”, not as it
was designed to be
· Data Collection:
§
Select15 reviewers and 10 tickets to be evaluated
§
Appropriate sampling techniques should be used
§
Each ticket is to be reviewed 2 times by each reviewer with a
gap of sometime (e.g. a week)
§
Analyze the data to verify the repeatability, reproducibility
and accuracy
· Frequency:
§
Once in a quarter
§
Addition of new reviewers in to the system
§
Changes to review checklists, Changes to the current process
being evaluated
§
Missing correlation with other sources like customer feedback
etc.,
SLA Prediction Model
Service Level Agreements (SLA) with the
customer is common in most of the service operations. SLA’s might vary
depending on the business need and many a times the Non Compliance to SLA’s
might lead to huge penalties as well as customer dissatisfaction.
This topic provides an approach for
predicting the SLA compliance in advance and helps in effectively managing the
SLA to avoid noncompliance as well as penalties. This is just an approach the
model can be adjusted based on the business rules, past trends, SLA compliance
parameters etc.
Scenario:
The team resolves the incident tickets received from the customer/automated
tools. The project has a committed SLA with the customer on the “Time to
Resolve the Issue”. And this Time to Resolve SLA is different for different
severity of the tickets. Each issue reported is associated with a knowledge
article that is been referred by the analyst to resolve the issue.
Model Approach:
·
Understand the SLA commitments
o
Time To Resolve – Time it took to
resolve the issue reported from the issue received i.e., Time To Resolve =
Issue resolved time – Issue reported time
o
SLA for Time Resolve
§
Severity 3 – 240 Minutes
·
Assess the parameters that might affect
the SLA
o
Parameters that might impact the Time To
Resolve includes
§
Severity
§
Issue type
§
Shift
§
Week Day/ Week End
§
KB Article
·
Analyze the issue categories
o
By Problem type
o
By KB article
·
Gather the data for the past 3-6 months
(Depending on the volume and issues coverage)
o
Below is the sample data captured for the Time To Resolve
SLA
·
Understand the Time To Resolve
distribution with respect to the above parameters as highlighted in second
bullet
o
Time To Resolve
§
Distribution with respect to
·
Confirm the parameters that are
impacting the Time To Resolve
o
Time To Resolve
§
Above table as observed there is a
significant variation in the distribution from Morning shift to Night shift
§
Confirmed parameters include
·
Issue Type
·
Shift
·
Baseline the Time To Resolve
distribution with respect to the above parameters
o
Time To Resolve – Baselines
·
Develop the Model to be referred/used
for predicting the SLA compliance. This can be customized based on the business
need
Tuesday, August 5, 2014
Consulting – Introduction to ITIL
Introduction:
•
Information Technology Infrastructure
Library
•
Global standard that has been in use for
over 20 years
•
Collection of best practices to optimize
the services
•
Started in 80s
•
v2 came along in
2000-2002
– Still Large and complex (8 Books)
– Talks about what you should do
•
v3 in 2007
– Much simplified and rationalized (5 books)
– Much clearer guidance & easier
– Aligned with ISO20000
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)