Showing posts with label Leadership. Show all posts
Showing posts with label Leadership. Show all posts
Saturday, November 22, 2014
Monday, July 28, 2014
Consulting – Taguchi’s Loss function
Myth: Any outcome
between the customer specification limits considered as equal form the customer
perspective. For example customer queue time in a bank is between 15-30minutes,
as per this myth the customer who is been served at 15 minutes and another
customer at 30minutes is received the same quality from the bank perspective as
both of them are service within the agree time.
Reality: The
quality of service/ product will be of not equal from the customer/ society
perspective as it goes away from the target value even though it is within the
agreed specification limits.
Justification:
Taguchi one of the well-known statistician / engineer developed a
representation that measures the financial impact of loss to the society if the
product/service deviates from the target value. The representation is termed as
Taguchi’s Loss Function. In conventional methods the Cost of Quality is
measured considering the number of products rejected or reworked. In this
method it is difficult to differentiate the cost of quality if the two products
properties are within the specification limits but vary from each other.
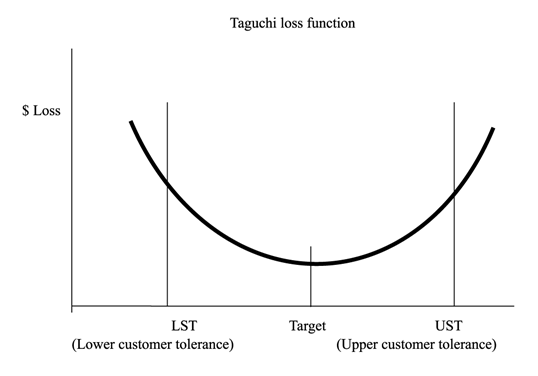
From Taguchi’s perspective the loss function is as below.
The graph depicts the lross function as a deviation from the target value of a
product parameter. The parameter could be a diameter, color, density, hardness
any other critical parameter of a product. From the service perspective the
parameter could be cycle time, communication, responsiveness etc.
UST – Upper Specification Tolerance, LST – Lower
Specification Tolerance
Taguchi believes performance begins decreasing gradually as
the design parameter deviates from the target value even though the parameter
value is between the LST and UST. Therefore, Taguchi proposed that the
loss function be measured by the deviation from the target value. The loss
function is
L = K * (Y – M) ^ 2
·
L is the result value of the function, generally
measured in monetary units
·
Y measured value
·
M target value
·
K is a loss coefficient (Convert into monetary
values)
Example: A company produces a part that has a diameter of 0.5
inches + or - 0.01 inches of tolerance. Failure cost of a rejection is $45.00.
There are 30 units produced and the actual diameter is as below. Calculate and
compare the loss considering the convention method as well as Taguchi’s loss
function method.
Saturday, July 12, 2014
Sunday, July 6, 2014
Friday, June 27, 2014
Thursday, June 26, 2014
Leadership – People
A candidate
for a news broadcasters post was rejected because of his voice. He was also
told that with his obnoxiously long name, he would never be famous.
-
Amitabh
Bachchan.
A small boy
– the fifth amongst several siblings of a poor father, was selling newspapers
in a small village to earn his living. He was not exceptionally smart at school
but was fascinated by religion and rockets. The first rocket he build crashed.
A missile that he built crashed multiple times and he was made a butt of
ridicule. He is the person to have scripted the space odyssey of India
single-handedly.
-
Dr.
APJ Abdul Kalam.
In 1962,
four nervous young musicians played their first record audition for the
executives of the Decca recording Company. The executives were not impressed.
While turning down this group of musicians, one executive said, “We don’t like
their sound. Groups of guitars are on the way out.”
- The group was called The
Beatles
In 1944,
Emmeline Snively, director of the Blue Book Modelling Agency told modelling
hopeful Normal Jean Baker, “You’d better learn secretarial work or else get
married.”
-
Marilyn
Monroe
In 1954m
Jimmy Denny, manager of the Grand Ole Opry fired a singer after one
performance. He told him, “You aren’t going’ nowhere…son. You ought to go back
to driving’ a truck.”
-
Elvis
Presley
When a
gentleman invented a communications machine in 1876, it did not ring off the
hook with calls from potential backers. After making a demonstration call,
President Rutherford Hayes said, “That’s an amazing invention, but who would
over want to see one of them?”
-
Alexander
Graham Bell
In the 1940s
another young inventor named Chester Carlson took his idea to 20 corporations,
including some of the biggest in the country. They all turned him down. In
1947, after seven years of rejections! He finally got a tiny company in New
York, the Halod Company, to purchase the rights to his invention an electrostatic
paper-copying process. Haloid became Xerox Corporation.
-
Chester
Carlson
A 4 year old
girl- the 20th of 22 children, contracted double pneumonia and
scarlet fever at a very early age, which paralyzed her left leg. Thereafter at
9 y ears of age she removed her leg braces and started walking without them. At
13 she decided to become a runner but kept failing miserably in all races that
she entered in. She kept trying inspite of several detractor and finally
started winning every race she entered.
-
Wilma
Rudolph, winner of 3 Olympic gold medals
A school
teacher scolded a boy for not paying attention to his mathematics and for not
being able to solve simple problems. She told him that he would not become
anybody in life. His mother, however believed in him and coached him in maths.
-
Albert
Einstein.
Wednesday, June 25, 2014
Six Thinking Hats
'Six Thinking Hats' a tool created by Edward de Bono is an
important and powerful technique used for decision making. This tool helps in
thinking outside the normal styles and guides you to consider the rounded view
of a situation. This is a very simple technique and easy to use, effective
parallel thinking process that increased the productivity. This tool, once learned can be applied
immediately!
This technique is build based on the principle of parallel
thinking which means at any moment everyone is looking in the same direction
and the direction is been changed until we reach the decision.
Six Thinking Hats technique can be used in meetings targeted for
a critical decision making. Each hat is a different style of thinking as
explained below:
White Hat
·
Neutral and objective, Focus on the
available data
·
Learn from the information that is
available
·
Analyze past trends from historical
data
·
Exclude opinions, feelings etc.,
·
Questions
o What do we know? What is missing? What
would we want to know?
·
Facts can be of two levels
o Believed facts, Verified facts
Red Hat:
·
Emotional and angry
·
Look at problems using intuition, gut
feelings
·
Understand the responses of people
·
Don’t expect any logical reasoning’s
for the feelings and justifications
Black Hat:
·
Consider all the negative points
·
Be cautious and defensive
·
Make your plans 'tougher' and more
resilient
·
Spot flaws and risks before the actions
·
Logically negative – Why this won’t
work?
Yellow Hat:
·
Best case scenario
·
Benefits
·
Think positively
·
Have an optimistic viewpoint to see
the benefits
Green Hat:
·
New ideas, concepts, creative
solution
·
Alternative solutions
·
Growth and fertility
·
Stands for creativity
·
No criticism of ideas
Blue Hat:
·
Cool and sky above
·
Control the decision making process
·
Move Green hat in case we are running
out of ideas
·
Move to black hat in case of
contingency
·
Organizes the thinking
How to use the hats:
·
Use any hat as needed and it can be
more than once
·
Sequence can be decided before the
meeting or it can be evolved as we progress
·
Not necessary to use every hat for
each decision making situation
·
Keep the time under each hat as short
·
Ensure discipline from each person
and can have ground rules set before the meeting
·
This tool can be used by individuals
and groups
·
Most used scenario - Open with a blue
hat and end with blue hat
o
Open with blue hat
§
Why are we here? What are we thinking?
What is the objective
§
Definition of the problem/situation
§
End state, Background or context
§
Plan the hats sequence
o
End with blue hat
§
What did we achieved
§
Outcome/Conclusion
§
Solution/Next steps
Summary:
Blue – Control & Organization of
thinking process
White – Objective facts and numbers
Red – Emotions and feelings
Yellow – Hope, Positive
Green – Creative and lateral
Black – Careful and cautious
Friday, June 6, 2014
Consulting Approach
In today’s world most of the work that we do in IT sector can be categorized into consulting. Even though the organizations have many roles but each role requires learning how to work as a consultant. Below tables shows the transition that can be expected from a normal role to a consultant
Consulting is about helping a project get from A to B
Consultants = change
Shift in:
From
|
Towards
|
Understanding : Value add/ Problem solving
| |
Approach : Reactive only
|
Approach : Proactive and Reactive
|
Skills : Need based and generic
|
Skills : Subject Matter Experts (SME)
|
Organization : Individual and customer pressured
|
Organization : Flexible/ Customer Centric/ Operational Focused
|
Model : Inbuilt/ learned
|
Model : Best Practices/ Industry Best Practices
|
Communication/ Interaction : Routine metrics or processes
|
Communication/ Interaction : Opportunities/ New areas / Workshops
|
Focus : Align with the situation
|
Focus : Align with delivery/ customer goals
|
Results : Invisible / Not
|
Results : Measurable and visible
|
Action plan:
1
|
Set the Expectations
|
2
|
Develop the SME Skills
|
3
|
Plan for communication/ Interaction
|
4
|
Research more on Problem Identification/ Solving
|
5
|
Set targets / Align with customer
|
6
|
Understand problems, Support with analytics
|
7
|
Develop programs that can be sustained
|
8
|
Shift from reactive to proactive
|
9
|
Quick workarounds/ Long term solutions
|
10
|
Highlight the patterns/ opportunities with advanced analytics/ Lean
|
11
|
Synchronizing with all the stakeholders
|
12
|
Enhance the skills (i.e., Problem solving, Lean/Six Sigma, Analytics etc.,)
|
13
|
Assessing/selecting/adopting Best practices outside or within organization
|
14
|
Focus on operational effectiveness/ efficiency in addition to customer expectations
|
Lead Without Title (LWT) - Book Notes
This article is created from the understanding/learnings from the book named “The Leader Who Had No Title” by Robin Sharma. This note presents the learning from the book in the way that I understood while reading this book.
· Lead without title (LWT) – to achieve this need to follow five rules represented in acronym called IMAGE
· IMAGE
o I – Innovation
o M- Mastery
o A – Authenticity
o G – Guts
o E – Ethics
· I – Innovation
o Making this day better than yesterday
o Great careers and great businesses are built by evolution and not by revolution. Slow and steady improvements that don’t look great in isolation becomes evolutionary over time with massive gains.
o Daily ripples of superior performance add up over time to a tidal wave of outrageous success.
o This can be done by anyone no matter what their career/lives
o Dream big yet start small and start now
o Small steps over time generate big results and at the same time the failures in case any do not lead to disaster.
o Like adding small amounts in bank from the childhood would give significant returns in the young age by the magic of compounding
· M – Mastery
o Committing yourself to mastery at what you do – whether your craft is selling staplers or educating children
o Be so good that people cannot ignore you – by comedian Steve Martin
o People said a structure i.e., Washington Monument this visionary could not be built. But the architect Robert Mills got the job done no matter what.
o “Nothing less than my very best” that’s what mastery
o Expect more from yourself than anyone around you could ever expect from you
o Our goal here, each and every day, is to be the best in the world at my craft and that’s how we continually move closer toward mastery.
o Every world-class expert has invested approximately 10000 hours (i.e., approx. 10 years) polishing their skills – from the Harvard Business Review article ‘The Making of an Expert’
o Beginning is hard – Space shuttle uses more fuel during its first three minutes after liftoff than during its entire voyage around the earth.
o A practical tool to use is ‘The Daily 5’ – Doing 5 little yet important focused acts every day to get you closer to your most important goals
· A – Authenticity
o In this radically new period of business, your ability to have an impact and make a contribution comes more from who you are as a person than from the authority you receive by your placement on some org chart
o Be who you are and say what you feel because those who mind don’t matter and those who matter don’t mind – by Dr.Seuss
o Don’t lose yourself on the way to top – by Jack Welch
o There will never be a better than you – by Warren Buffett
o Being authentic isn’t just being trustworthy, staying true to your mission and values, and speaking honestly. It’s clear that you are also saying that being authentic means realizing all my potential and really getting to know all that genius you said was inside me.
o When you give yourself permission to be open, real and brilliant around others, you give others permission to be open, real, and brilliant around you.
o Authenticity about being true to who you are , even when everyone around you wants you to be someone else – by basketball great Michael Jordan in the book “Driven from Within”
o Rather than defining their success by what they get, Leaders define their success by what they give
· Guts
o To have guts to see the opportunities where others see challenges and to envision things becoming a whole lot better while others grow complacent it to become a visionary
o Criticism is the defense reaction that scared people use to protect themselves against change
· Ethics
o You will never go wrong in doing what’s right.
o Leadership success lies at the intersection where excellence meets honor
o How well you make your sheets determine how well you’ll sleep in your bed
Subscribe to:
Posts (Atom)