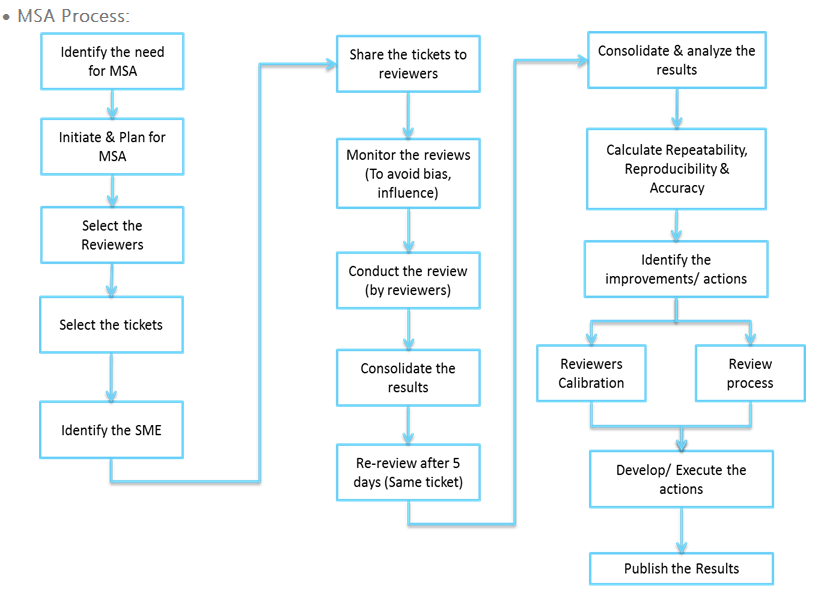
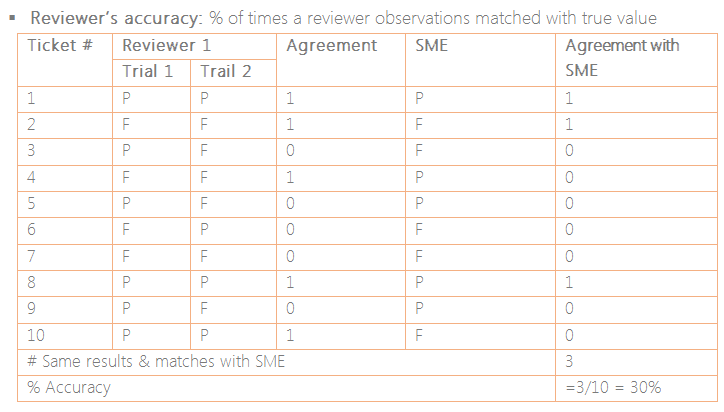
Context: In this scenario the incident tickets were reviewed by
the selected and trained reviewers with respect to a predefined
parameters. The main objective is to
understand the accuracy as well as the consistency among the reviewers before
confirming the review results followed by appropriate actions.
v
Reviewers, Checklist, Environment, Review method, Data
collection/capturing
Components
of MSA Process:
·
Key Considerations:
§
The study should be performed over the range (Severities,
Shifts, Reviewers, Towers etc.,)
§
Actual Checklist should be used, already written review
procedures should be followed
§
It should be business as usual
§
Measurement variability should be presented “as-is”, not as it
was designed to be
· Data Collection:
§
Select15 reviewers and 10 tickets to be evaluated
§
Appropriate sampling techniques should be used
§
Each ticket is to be reviewed 2 times by each reviewer with a
gap of sometime (e.g. a week)
§
Analyze the data to verify the repeatability, reproducibility
and accuracy
· Frequency:
§
Once in a quarter
§
Addition of new reviewers in to the system
§
Changes to review checklists, Changes to the current process
being evaluated
§
Missing correlation with other sources like customer feedback
etc.,