Many techniques available in conducting Root
Cause Analysis, each technique has its own advantages and suitable for a
particular situation. Common, widely accepted and simple to use techniques
includes
·
Cause & Effect diagram
·
5-Why Analysis
·
Brainstorming
Cause &
Effect Diagram: Also
called as Fishbone diagram. This is a tool for identifying all the causes of an
effect. The effect being examined is the problem/opportunity that has to be
eliminated. C&E Diagram is a graphical representation of the causes and
effect. Use this technique for
·
Multiple causes has to be grouped logically
·
Understand width and depth of the causes
·
Problem is repetitive
Steps:
·
Write down the effect to be investigated and
draw the backbone arrow (as below)
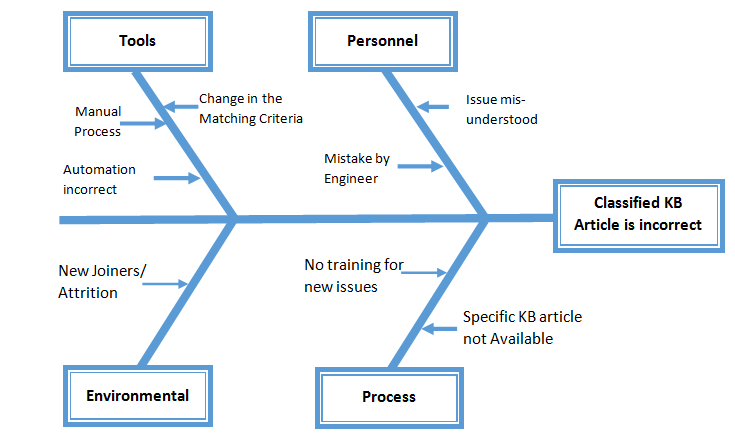
Note: KB Article – Knowledge Base Article
has to be selected by the engineer to resolve an issue reported by the
customer. Selecting of wrong article either delays the resolution or
unnecessary escalation to a next level as the issue is unresolved by the engineer.
· Brainstorm with the identified people
considering all the broad areas/ groupings of the potential causes of the
effect “Classified KB article is incorrect”. Rule of thumb consider the generic
4 categories i.e., Man, Method, Material and Environment. You can define your
own categories and may use affinity diagram to group the cause.
·
Group the causes identified during the
brainstorming into logical groupings to represent the Cause & Effect
relationship.
·
Drill Down all the causes for further reasons
and goon extending the branches till the root cause is identified (May use
5-Why technique as required)
Five – Why
Analysis: 5-Why is a
problem solving technique that allows us to reach the root cause by repeatedly
asking the questions. Even though this technique is called “5-Why” we may reach
the root cause with fewer or more than five questions. Use this technique
·
Repetitive
issue without any supporting data
·
Simple
and low risk problems that does not require significant analysis
·
Problem
is very specific to a process/ system (Not spread to multiple processes)
Steps:
·
Define
the problem
·
Gather
the team and confirm the problem
·
Ask
the first Question Why? Record all the answers on a whiteboard or flipchart
·
Ask
few more successive “Why” until we reach no further causes
·
Confirm
the root cause and proceed for next set of actions
Example: Customer complaints on the delay in Pizza delivery
·
Why there is a delay
in the Pizza delivery?
o Delivery boy not reached on time
·
Why the delivery boy
not reached on time?
o He could not find the address
·
Why he could not find
the address?
o Address given to him is incorrect
·
Why the address is
incorrect?
o Address is not available in the records
·
Why the address is
not available in the records?
o Customer is new, manually note down the address
·
Why the address is
incorrect?
o Incorrectly noted while taking orders
Solution: Incase of the first
time users, confirm the address once again and provide the telephone numbers to
the delivery boy to reach out to the customer in case of any issues.
Brainstorming: One
of the very widely used and easy to use techniques for analyzing the problem to
reach the root causes. Brainstorming generates ideas and later evaluated to finalize
and confirm the causes.
Steps:
·
Establish
a clear objective, Re-phrase for confirmation
·
Create
a list of questions
·
Document
all the findings and agree on the same




No comments:
Post a Comment